The limitations of voluntary climate commitments from private financial actors
(This document was initially published in November 2022).
Private finance will not fund the transition without a stronger commitment from public authorities
According to Mark Carney’s statements at COP 26, the Glasgow Finance Alliance for Net Zero – GFANZ, an unprecedented voluntary coalition of 500 financial actors with $130 trillion in assets – was destined to be a game-changer in financing the transition to a carbon neutral economy.
But can we rely primarily on this voluntary approach? The answer presented in this Climate Brief is no. Although useful and led by people who are truly committed to the cause, we cannot expect too much from these initiatives to mobilize private financial actors in favour of the given the intrinsic limitations to their effectiveness. Conversely, an approach based primarily on the strong commitment of public authorities seems essential.
This public commitment must be based on a wide range of instruments, including financial regulation, whose role is essential when it comes to financial actors.
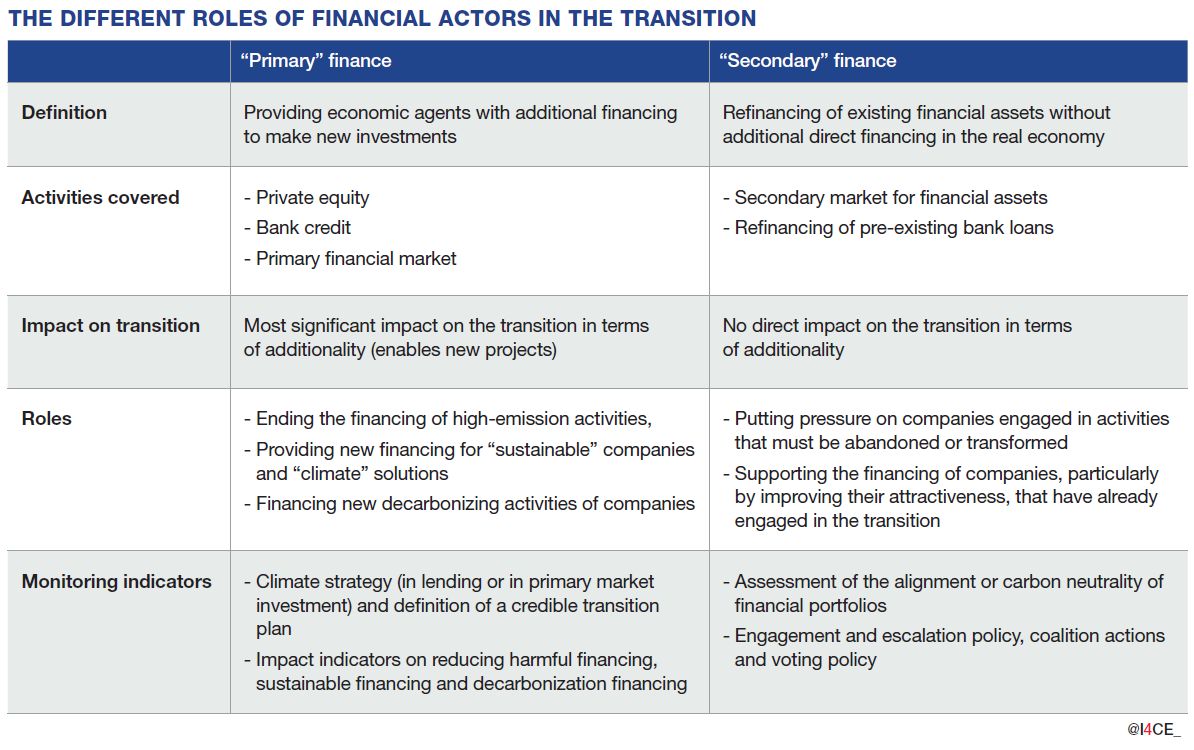
The first section of this document analyses what we can realistically expect from financial actors in terms of funding the transition. The second section presents the reasons why voluntary private initiatives cannot play a decisive role, despite the impressive volume of assets managed by the actors who have made these commitments. The third section returns to the decisive role of public authorities in mobilizing private finance.
This report is part of the Finance ClimAct project and was produced with the contribution of the European Union LIFE programme. This work reflects only the views of I4CE – Institute for Climate Economics. Other members of the Finance ClimAct Consortium and the European Commission are not responsible for any use that may be made of the information it contains.


