Financing the climate transition in France: what room for manœuvre on public funding needs?
Report only available in French
France is facing a climate investment deficit relative to its climate objectives. Today, these investment are already putting a strain on public finances, whether in terms of investing in public facilities or co-financing projects by households and business. Increasing climate investments is therefore a challenge for public finances. But the scale of the challenge varies, depending on future policies. So what room for manoeuvre is there in terms of climate-related public spending needs?
In this report, we analyse the options for allocating public and private funding to achieve France’s climate investment targets identified in the Landscape of Climate Finance in France, on the basis of the draft national low-carbon strategy (SNBC) currently under review.
Private finance cannot be summoned by decree. Today, households and businesses often lack a viable economic model for their climate investments. And what the private sector cannot do, the public sector will have to fund. Thus, in the face of the climate investment deficit and without action to limit spending, the need for additional public spending would reach €71 billion in 2030.
However, this funding need can be reduced by deploying a variety of measures: tightening regulations, eliminating certain tax provisions, refocusing aid on the lowest-income beneficiaries, but also increasing energy saving certificates (CEE) or user service charges. Combining all these measures, which shift the burden of financing onto households and businesses, the minimum additional public spending required is €39 billion, of which €18 billion is for the State. At this lower level, the public funding need is restricted to public facilities, such as administrative and school buildings and transport infrastructures.
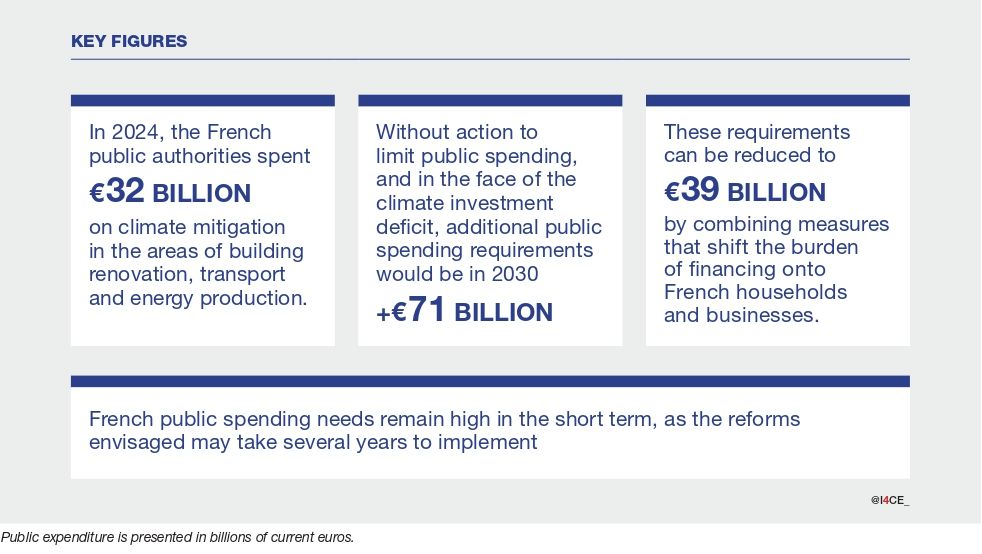
Looking ahead to 2030, there is considerable room for manoeuvre in terms of public spending requirements in France. Nevertheless, they remain high in the short term, as the reforms envisaged to curb them may take several years.
The orders of magnitude of the climate-related public spending needs can inform the preparation of the future multiannual financing strategy for the ecological transition, expected in France this autumn. The strategy will have to take account of the effectiveness of the instruments available, as well as the fair distribution of the funding. Between the top and bottom of the range, intermediate options are possible. It should be noted that other financing options exist, but they have not been included in this exercise due to the obstacles outlined at the end of this note.
This publication summarises the initial results of the Financing Scenarios project, which may be further developed in the autumn.




