Estimating greenhouse gas emissions from food consumption: methods and results
A large share of global greenhouse gases (GHG) emissions comes from food production and consumption. Measuring the total footprint of world diets remains however a challenge. The main reason is the lack of harmonization on consumption based emission accounting methods. While a few estimates are available, their results are often hardly comparable, may be rather different and sometimes contradictory.
In this study “Estimating greenhouse gas emissions from food consumption: methods and results”, I4CE presents the range of consumption based emission accounting methods, their benefits or limits, and their results.
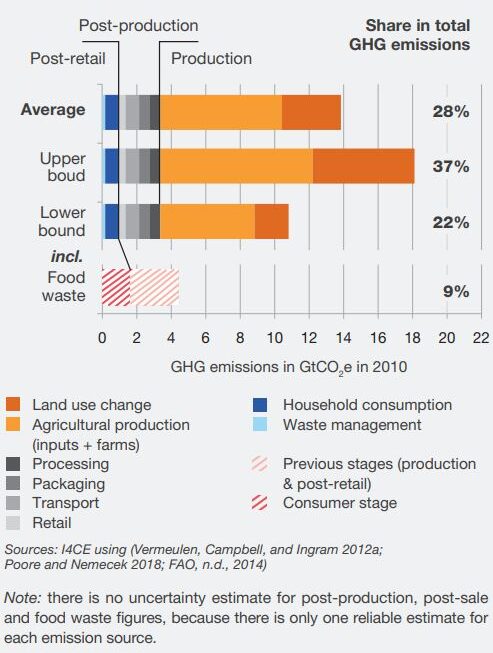
By combining existing studies, we estimate that GHG emissions from food consumption in 2010 were around 13,8 GtCO2e (± 3,6 GteqCO2), i.e. 28% of global emissions, all sectors combined. Around 75% of GHG are emitted during the production phase, 15% between the farm gate and the retail store, and 10% after retail.
Animal products (excl. marine products) are responsible for 63% of total food emissions. Ruminant animals (cattle, goats and lamb) represent the essential part of this amount.
Comparison of GHG emissions from total food vs. animal products only